Microsoft Visual C++ Compiler For Python 3.7 Download UPDATED
Microsoft Visual C++ Compiler For Python 3.7 Download
Python in Visual Studio Code
Working with Python in Visual Studio Code, using the Microsoft Python extension, is simple, fun, and productive. The extension makes VS Code an excellent Python editor, and works on any operating system with a diversity of Python interpreters. Information technology leverages all of VS Code'due south power to provide machine complete and IntelliSense, linting, debugging, and unit testing, along with the power to easily switch between Python environments, including virtual and conda environments.
This article provides only an overview of the different capabilities of the Python extension for VS Code. For a walkthrough of editing, running, and debugging code, use the push beneath.
Python Hello World Tutorial
Install Python and the Python extension
The tutorial guides yous through installing Python and using the extension. You must install a Python interpreter yourself separately from the extension. For a quick install, use Python from python.org and install the extension from the VS Code Market.
Once yous have a version of Python installed, activate it using the Python: Select Interpreter command. If VS Code doesn't automatically locate the interpreter yous're looking for, refer to Environments - Manually specify an interpreter.
You tin configure the Python extension through settings. Learn more in the Python Settings reference.
Windows Subsystem for Linux: If you are on Windows, WSL is a great way to do Python development. You can run Linux distributions on Windows and Python is often already installed. When coupled with the Remote - WSL extension, you get full VS Lawmaking editing and debugging support while running in the context of WSL. To larn more than, become to Developing in WSL or try the Working in WSL tutorial.
Run Python code
To experience Python, create a file (using the File Explorer) named hello.py and paste in the following code:
print ( "Hello World" ) The Python extension then provides shortcuts to run Python lawmaking in the currently selected interpreter (Python: Select Interpreter in the Command Palette):
- In the text editor: correct-click anywhere in the editor and select Run Python File in Terminal. If invoked on a selection, but that selection is run.
- In Explorer: right-click a Python file and select Run Python File in Terminal.
You can also use the Last: Create New Final command to create a terminal in which VS Lawmaking automatically activates the currently selected interpreter. See Environments below. The Python: Start REPL activates a final with the currently selected interpreter and so runs the Python REPL.
For a more specific walkthrough on running lawmaking, meet the tutorial.
Autocomplete and IntelliSense
The Python extension supports code completion and IntelliSense using the currently selected interpreter. IntelliSense is a general term for a number of features, including intelligent code completion (in-context method and variable suggestions) across all your files and for born and third-party modules.
IntelliSense quickly shows methods, class members, and documentation equally you type, and y'all can trigger completions at whatever time with ⌃Space (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Space). You lot can also hover over identifiers for more information nearly them.
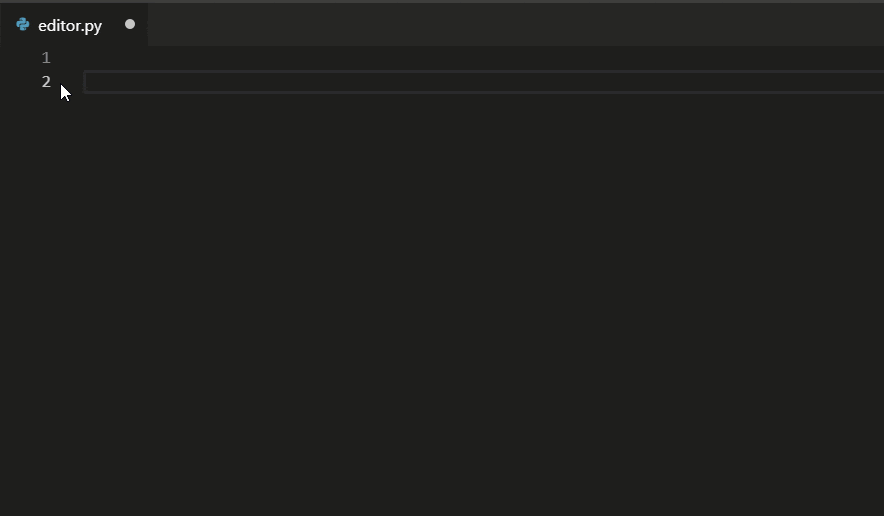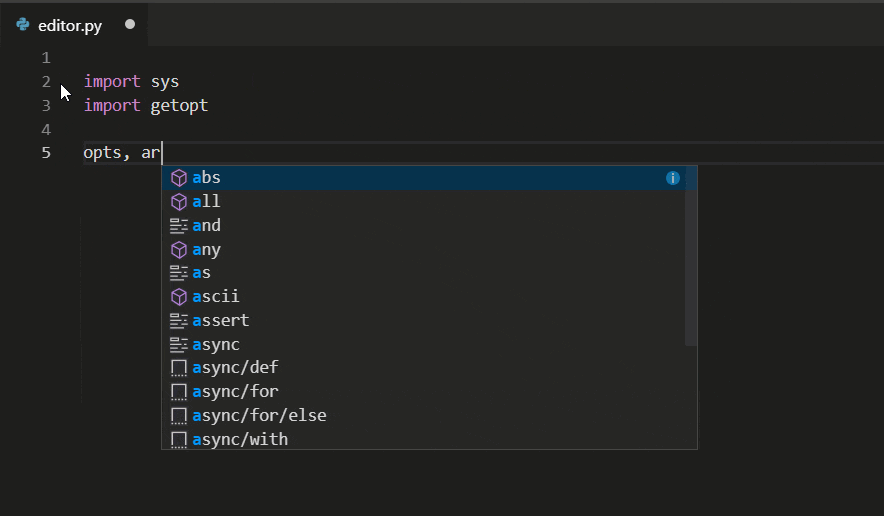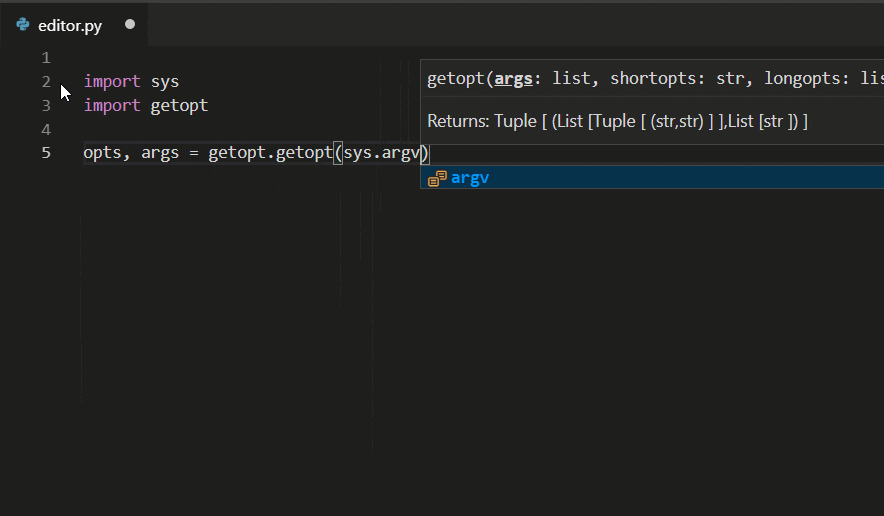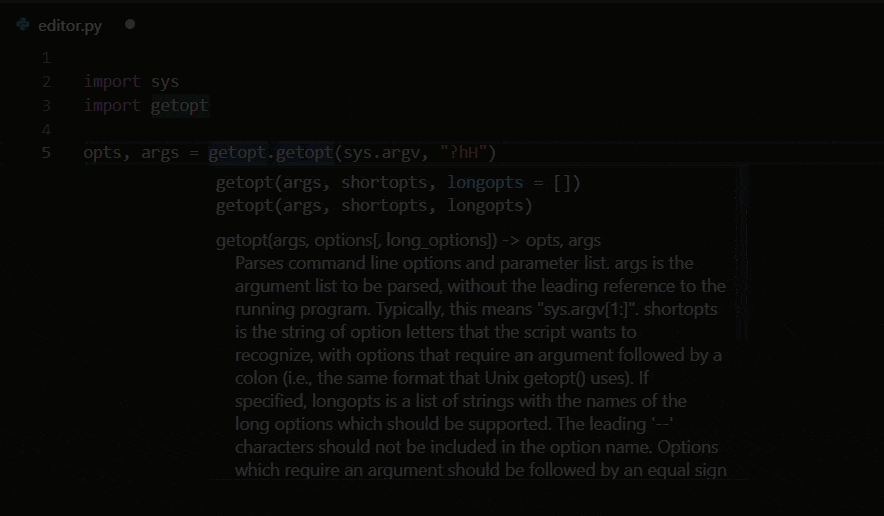
Tip: Check out the IntelliCode extension for VS Lawmaking (preview). IntelliCode provides a set of AI-assisted capabilities for IntelliSense in Python, such as inferring the nearly relevant auto-completions based on the electric current lawmaking context.
Linting
Linting analyzes your Python code for potential errors, making it easy to navigate to and correct unlike problems.
The Python extension tin can apply a number of unlike linters including Pylint, pycodestyle, Flake8, mypy, pydocstyle, prospector, and pylama. Come across Linting.
Debugging
No more print statement debugging! Set breakpoints, inspect data, and use the debug console as you lot run your program step by step. Debug a number of different types of Python applications, including multi-threaded, spider web, and remote applications.
For Python-specific details, including setting up your launch.json configuration and remote debugging, see Debugging. Full general VS Code debugging data is constitute in the debugging document. The Django and Flask tutorials too demonstrate debugging in the context of those web apps, including debugging Django page templates.
Environments
The Python extension automatically detects Python interpreters that are installed in standard locations. It as well detects conda environments as well as virtual environments in the workspace folder. See Configuring Python environments.
The current environment is shown on the left side of the VS Code Status Bar:

The Status Bar also indicates if no interpreter is selected:
The selected environs is used for IntelliSense, auto-completions, linting, formatting, and any other language-related characteristic other than debugging. Information technology is as well activated when you employ run Python in a concluding.
To modify the current interpreter, which includes switching to conda or virtual environments, select the interpreter proper name on the Status Bar or use the Python: Select Interpreter command.
VS Code prompts you with a listing of detected environments too as any yous've added manually to your user settings (see Configuring Python environments).
Installing packages
Packages are installed using the Last console and commands similar pip install <package_name> (Windows) and pip3 install <package_name> (macOS/Linux). VS Code installs that package into your projection forth with its dependencies. Examples are given in the Python tutorial too as the Django and Flask tutorials.
Jupyter notebooks
If you open a Jupyter notebook file (.ipynb) in VS Lawmaking, you can use the Jupyter Notebook Editor to directly view, change, and run lawmaking cells.
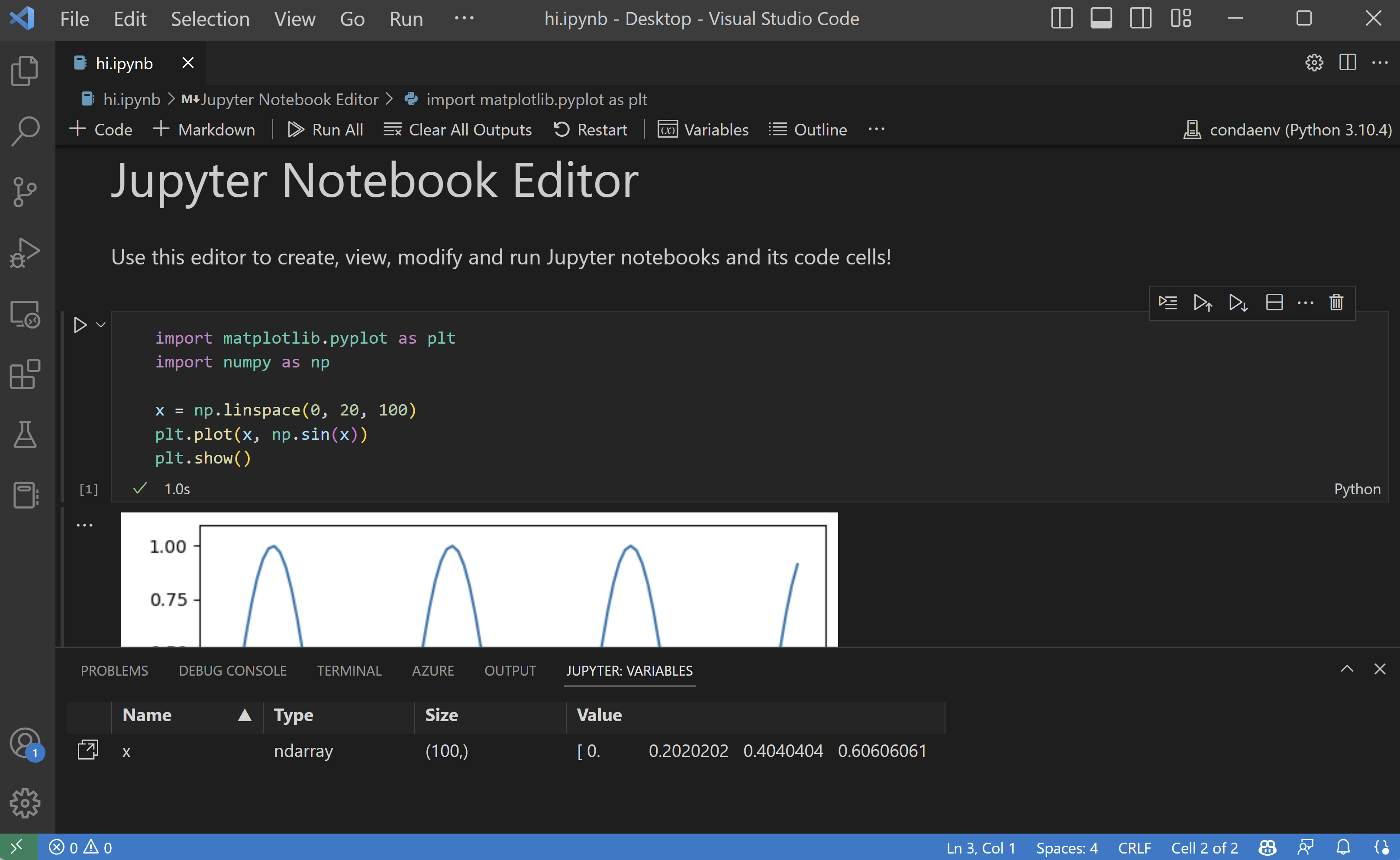
You can also convert and open the notebook as a Python code file. The notebook's cells are delimited in the Python file with #%% comments, and the Python extension shows Run Prison cell or Run All Cells CodeLens. Selecting either CodeLens starts the Jupyter server and runs the cell(due south) in the Python interactive window:
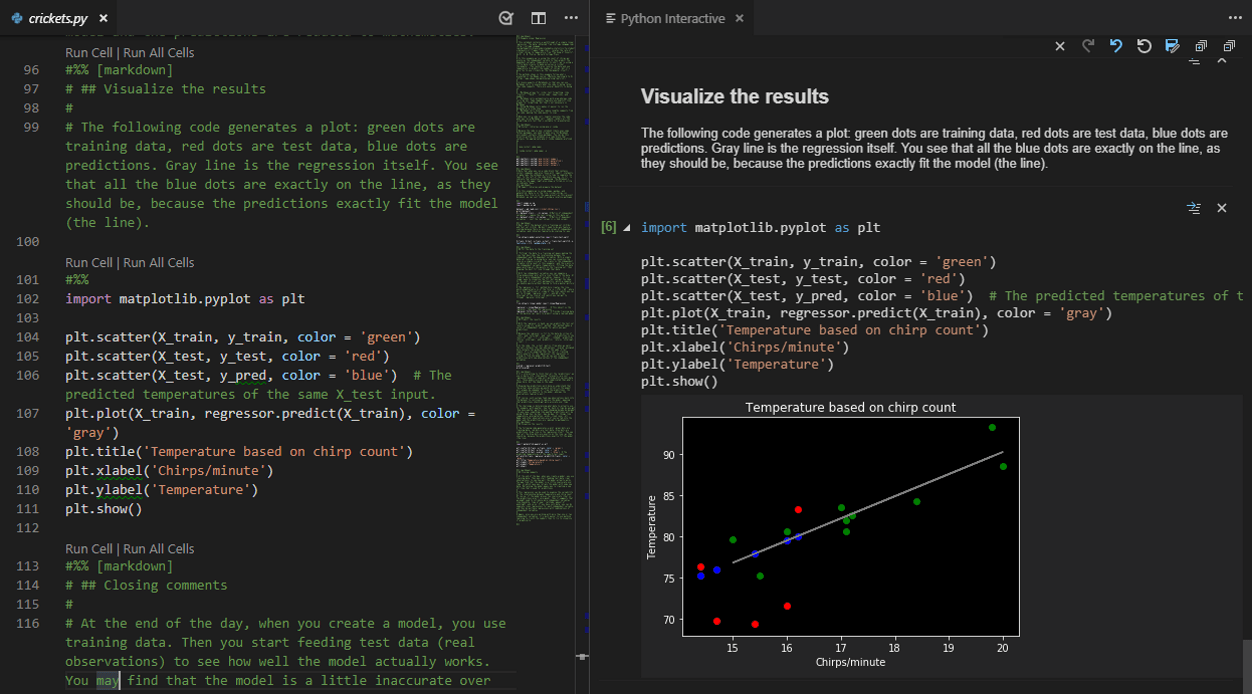
Opening a notebook as a Python file allows you to utilize all of VS Lawmaking'due south debugging capabilities. You can then save the notebook file and open information technology again every bit a notebook in the Notebook Editor, Jupyter, or fifty-fifty upload it to a service similar Azure Notebooks.
Using either method, Notebook Editor or a Python file, y'all can also connect to a remote Jupyter server for running the code. For more information, run into Jupyter back up.
Testing
The Python extension supports testing with unittest and pytest.
To run tests, you enable one of the frameworks in settings. Each framework also has specific settings, such equally arguments that identify paths and patterns for test discovery.
One time discovered, VS Code provides a diverseness of commands (on the Status Bar, the Command Palette, and elsewhere) to run and debug tests, including the ability to run private exam files and private methods.
Configuration
The Python extension provides a broad variety of settings for its various features. These are described on their relevant topics, such as Editing lawmaking, Linting, Debugging, and Testing. The consummate list is found in the Settings reference.
Other popular Python extensions
The Microsoft Python extension provides all of the features described previously in this article. Additional Python language back up tin be added to VS Code by installing other popular Python extensions.
- Open the Extensions view ( ⇧⌘10 (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+X)).
- Filter the extension listing by typing 'python'.
The extensions shown above are dynamically queried. Click on an extension tile above to read the description and reviews to decide which extension is best for you. Encounter more in the Market place.
Adjacent steps
- Python Hello World tutorial - Get started with Python in VS Code.
- Editing Python - Larn about auto-completion, formatting, and refactoring for Python.
- Basic Editing - Larn about the powerful VS Code editor.
- Code Navigation - Motility quickly through your source lawmaking.
- Django tutorial
- Flask tutorial
DOWNLOAD HERE
Posted by: myershimince.blogspot.com
